60% of social housing residents are in jobs at high risk from automation

@Clarion_Group report warns that automation could take 1.1 million social housing residents’ jobs
- Cost of living crisis set to hit social housing residents hardest.
- 3 in 4 social renters never worked from home, even at the height of the pandemic.
- To make levelling-up work for England’s 10.5 million social housing residents, the Royal Society for Arts, Manufactures and Commerce (RSA) calls for a new ‘Social Housing Plus’ model.
Social Security: Automation and economic security among England’s social renters is authored by the RSA and has been developed in partnership with Clarion Housing Group, the largest social landlord in England.
Clarion runs a national employment programme open to social housing residents, supporting thousands of people into employment and training every year.
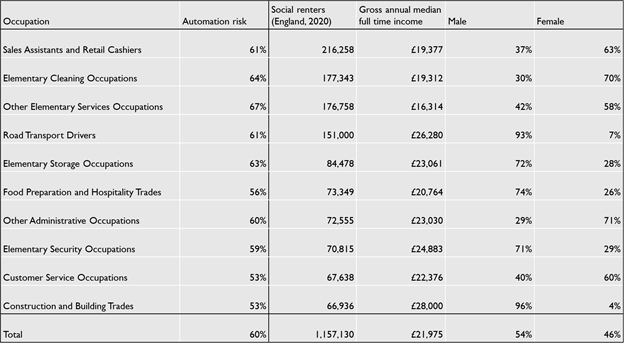
The report, which is the first study to explore the relationship between housing tenure and automation, finds:
- 1,157,000 social housing residents’ jobs are at high risk: some of the most at-risk roles include retail (which employs 216,000 social residents), cleaning (177,000), elementary service roles (176,000), road transport (151,000) and storage (84,000). See Notes for full table.
- Overall, 61% of social residents in work are in jobs at high risk from automation, compared to 43% of private renters and 35% of owner occupiers.
- Social housing residents are much less likely to have jobs that allow them to work from home: 74% of social residents did not work from home at the height of the pandemic, compared to 46% of owner occupiers and 56% of private renters, new RSA analysis of official ONS data shows. The RSA says that this indicates increased risk from the changing world of work, as working from home becomes part of many roles.
- Social housing residents face a tougher cost of living crisis: wages for social housing residents are set to fall in real terms, the RSA’s research finds, as fewer than four in ten (38%) of social renters receive an annual incremental pay increase, six percentage points fewer than both owner occupiers and private renters. Meanwhile 41% are ‘just about managing’ financially, compared to 33% in the private rented sector, and 13% of owner occupiers.
- Social housing itself is an important lever against economic insecurity: qualitative interviews, carried out as part of the research, showed that many especially valued their social rented home during periods of personal crisis, including the Covid-19 pandemic.
The report calls on the UK government to:
- Agree a ‘Social Housing Plus’ model extra support for England’s 10.5 million social housing residents. Led by the local authority and supported by housing associations where possible, the ‘Social Housing Plus’ model would work to ensure all social renters are able to access the local services they need to improve their economic security.
- Provide a more comprehensive offer of maintenance grants and bursaries for adult learners in the social housing sector, as part of the lifetime skills guarantee.
- Grow the UK social housing stock, ensuring 30% of all new homes are for social rent.
- Pilot ‘guaranteed income’ welfare schemes to explore whether ending benefits sanctions increases employment.
David Avery, Chair of Clarion Housing Group, said:
“Clarion supports thousands of our residents into work every year, but we know from experience that many have insecure finances and are facing challenges in the changing world of work.
“This new report confirms that many people in social housing will need to retrain and will require financial support to do so. That’s why we’re calling on government to provide a comprehensive offer of maintenance grants and bursaries for adult learners, as part of the Lifetime Skills Guarantee.”
Jake Jooshandeh, RSA researcher and lead report author, said:
“If the levelling-up agenda is to help social housing tenants, we need to see real action on the twin risks of automation and the cost-of-living crisis – both of which will hit this group harder without more support.
“Automation could be an opportunity for social housing tenants, but this will require change. Housing associations and councils are essential to promoting greater economic security, but this extra work must be fully funded by national government.”
Methodology: This research is predominantly based on original RSA analysis of data publications of the Understanding Society dataset and the Labour Force Survey.











Responses