95% Teachers say SATs are harmful to mental health
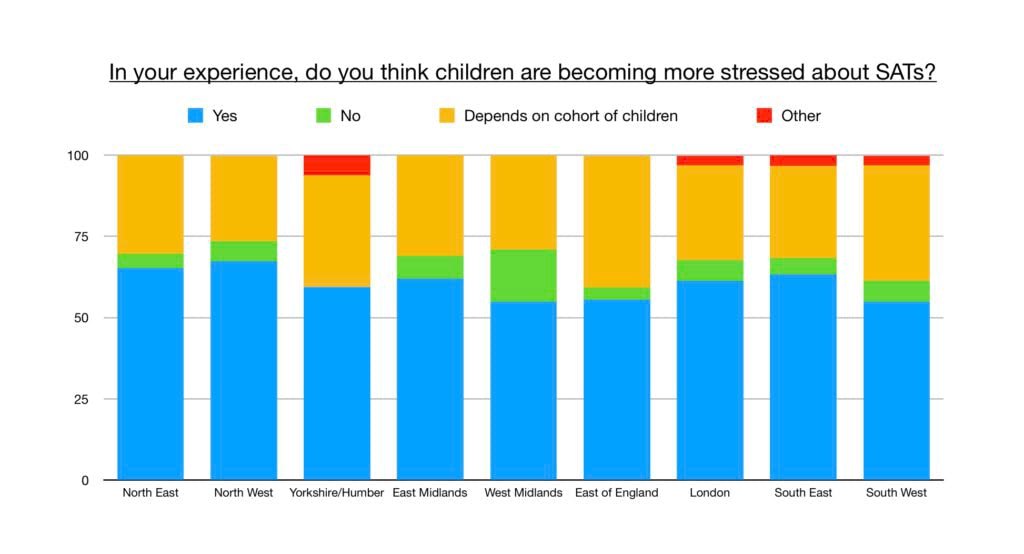
Over 95 percent of Teachers and Teaching Assistants believe that young children are becoming increasingly stressed by SATs, the government tests pupils must take in both Year 2 and Year 6 of primary school.
Among the disturbing responses to the stress of the tests seen frequently by the hundreds of teachers surveyed were children feeling sick, not wanting to come to school, being teary, anxious, having problems sleeping, headaches, bed-wetting, and displaying emotional outbursts, negative changes in behaviour and low self-confidence.
The survey, by lesson-planning and resources experts PlanBee, comes as Labour leader Jeremy Corbyn vows that a Labour government would scrap SATs, saying that young children should not be subjected to ‘extreme pressure testing’.
One teacher who replied to the survey said: ‘I’ve seen a Year 2 child cry during the test. This was an able child. I had to tell him how amazing he was and that what he did in the test did not matter because I already knew how good he was.’
Another reported ‘nervous fidgeting during teaching and follow-on work, increased sensitive behaviour, lack of motivation/interest in the curriculum, parents reporting they [the child] didn’t want to come to school’.
The survey shows that teachers are equally opposed to the tests across the country, with few regional variations. But opposition was highest in the North West and lowest in the West of England and the South West.
When asked if Year 2 children should revise for SATs, 75.3% of respondents disagreed or strongly disagreed that children should be revising at all, with less than 10% of respondents agreeing or strongly agreeing that they should revise.
The attitude to revision by Year 6 pupils was only slightly less hostile, with 50.8% believing they should not revise. Twenty-six percent said that at this stage children should definitely revise, the remaining 23.3% taking a middle view, suggesting they favour less intensive revision sessions than many schools currently provide.
Very few schools allow their pupils to undertake SATs with little or no preparation. So should children as young as six be aware that they are revising for an ‘important’ test?
An overwhelming 85.9% of respondents agreed or strongly agreed that Year 2 children should not be aware they are revising, compared to 48.1% for Year 6.
Only 6.3% disagreed or strongly disagreed that Year 2 children should not know they are revising, compared to 29.3% for Year 6.
Former teacher Becky Cranham of lesson planners PlanBee, which carried out the survey of 334 teaching professionals , said the results showed that teachers had overwhelmingly negative attitudes towards SATs preparation for young children and were very fearful of its impact on their mental health.
‘One would hope that subjecting children to rigorous, standardised testing would be used to help further the children’s education, assess pupil attainment and improve learning. Alas, this does not seem to be the case. A whopping 87.5% of our respondents believed that the primary purpose of SATs was to assess school performance.’
Only 2.7% of respondents said the purpose of the tests was to inform setting for Year 3 or Year 7 and just 4.2% believed it was to assess and improve pupil learning.
She added: ‘We know that many children are becoming more stressed about SATs at a time when they should be enjoying the broad and balanced curriculum that Ofsted agrees enables children to achieve most successfully in their school careers. However, the pressure put on teachers to achieve particular SATs results – and the subsequent pressure teachers then have to put on their pupils – means that in reality many curriculum areas are pushed aside in favour of ensuring children are ready for the tests, particularly in Year 6.
Ms Cranham said that in her experience, parents were swayed by Ofsted rankings rather than SATs results and queried who was actually benefitting from the annual ordeal.











Responses